Understanding the Importance of Childhood Theorists
Childhood theorists play a pivotal role in early childhood education and care settings, they guide our practices and helping us create meaningful and effective learning experiences. By studying the works of these theorists, we gain insights into child development, learning processes, and the factors that influence children’s growth. This knowledge empowers us to design age-appropriate curricula, environments, and strategies that promote holistic development and cater to the unique needs of each child.
You may wonder why childhood theorists, both historical and contemporary, remain relevant in our profession today? Well, in essence, their theories provide a solid framework for understanding and supporting children’s development. By integrating their insights into our practices, we ensure that our early years learning environments are grounded in research, tailored to the individual child, and promote holistic growth
The Standout Theorists That Shaped Our Profession
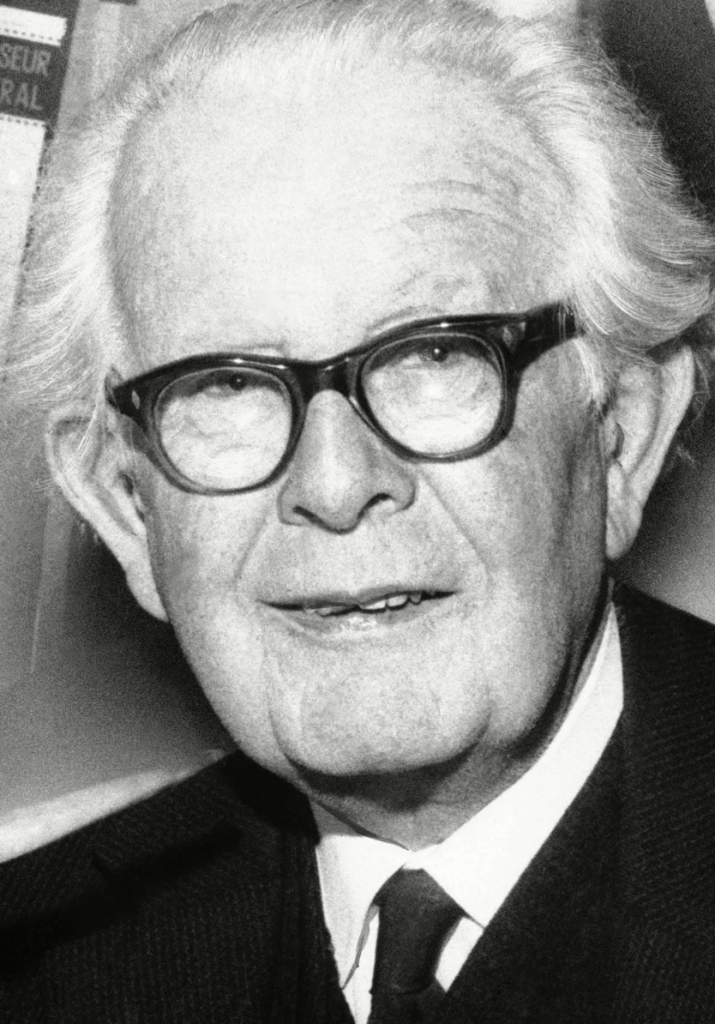
Jean Piaget (1896-1980)
Renowned for his cognitive development theory, Jean Piaget emphasized that children construct knowledge through their active interactions with the world. His stages of cognitive development, such as sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, and formal operational, continue to shape our understanding of how children think and learn at different ages.
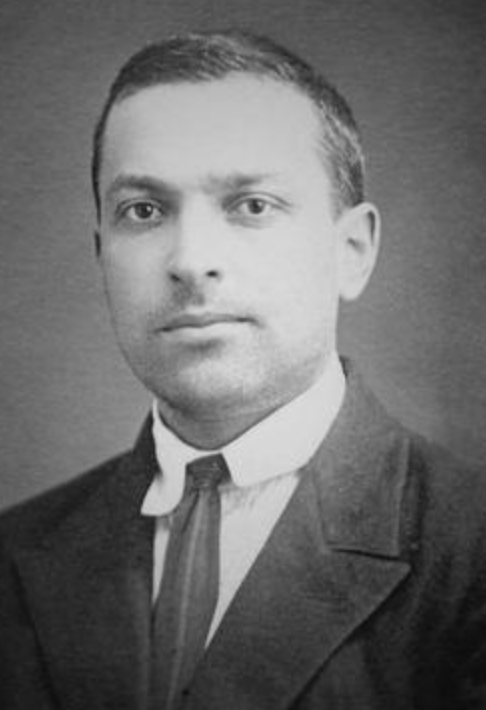
Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934)
Lev Vygotsky’s sociocultural theory emphasized the role of social interactions, language, and cultural context in shaping children’s learning. His concept of the “zone of proximal development” highlights the importance of providing appropriate scaffolding and support to help children reach their full potential.
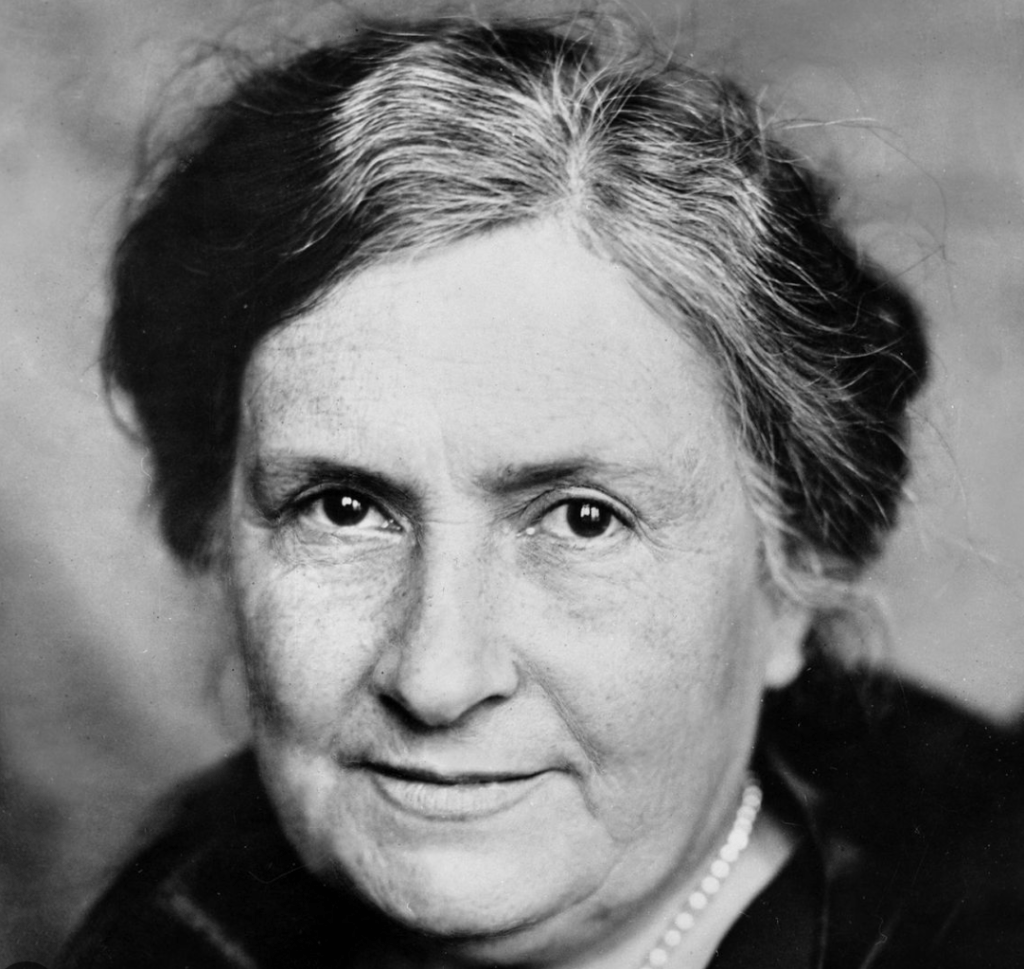
Maria Montessori (1870-1952)
Maria Montessori’s pioneering work introduced a child-centred approach to education, emphasizing independence, hands-on learning, and self-discovery. Her method has influenced early years learning environments worldwide, promoting a sense of autonomy, concentration, and intrinsic motivation.
Erik Erikson (1902-1994)
Erik Erikson’s psychosocial theory focused on the stages of psychosocial development throughout the lifespan. His emphasis on the importance of identity formation, social interactions, and emotional well-being helps us understand and support children’s socio-emotional growth during the early years.
Contemporary Childhood Theorists
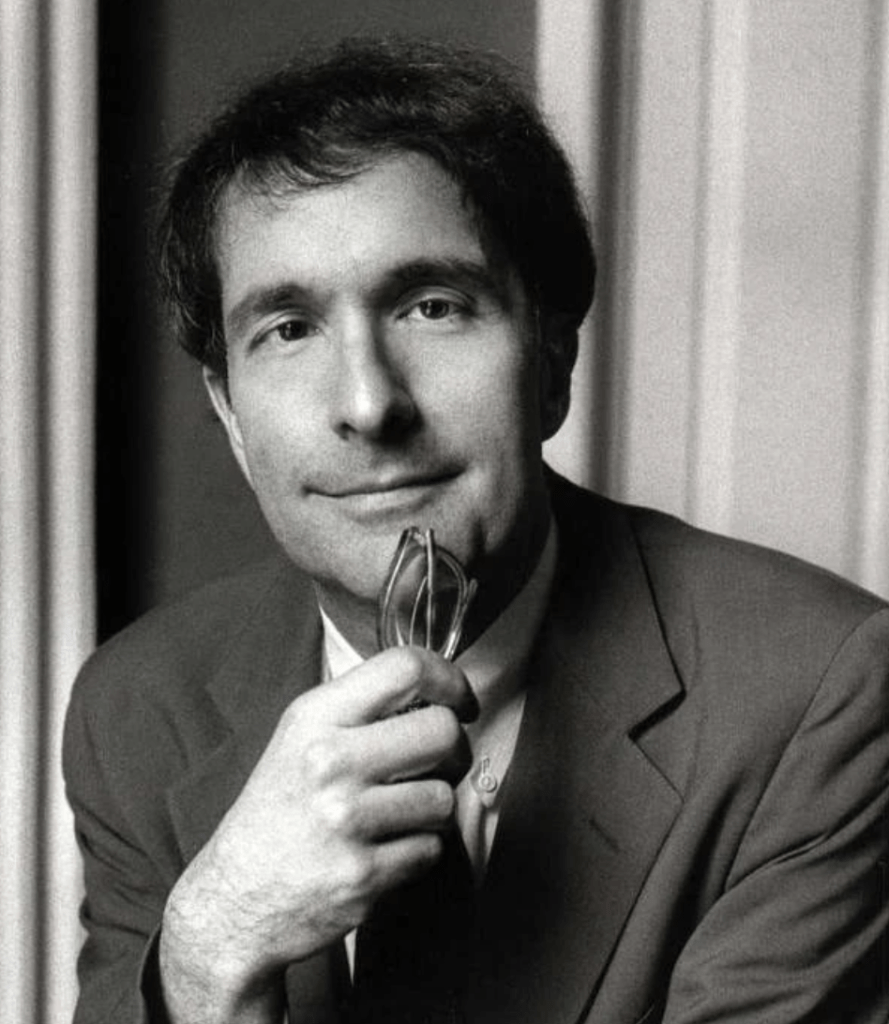
Howard Gardner (1943-Today)
Howard Gardner’s theory of multiple intelligences expanded our understanding of intelligence beyond traditional measures. He proposed that individuals possess various types of intelligences, including linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, musical, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalistic. Gardner’s theory reminds us to value and cater to the diverse strengths and abilities of children.
Urie Bronfenbrenner (1917-2005)
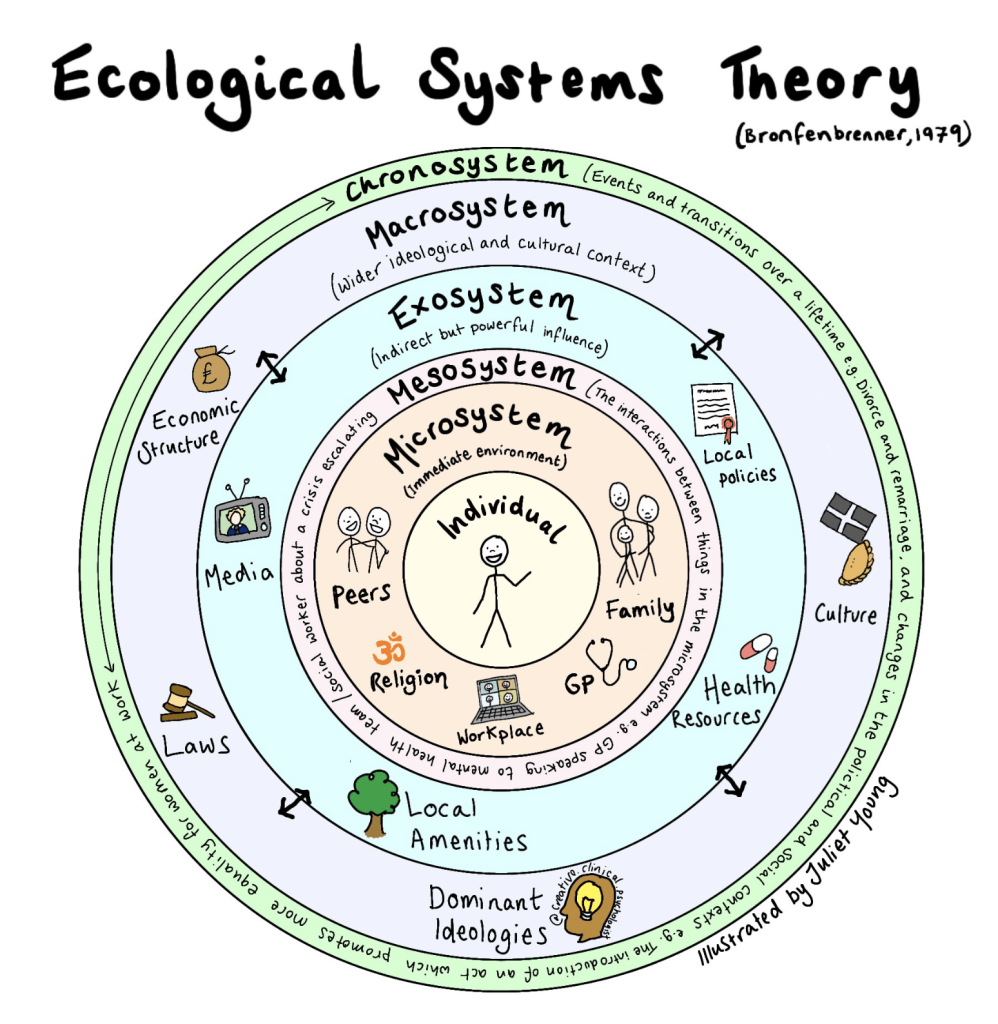
Urie Bronfenbrenner’s ecological systems theory emphasizes the interconnectedness of a child’s environment and its influence on their development. He proposed multiple systems, including the microsystem, mesosystem, exosystem, and macrosystem, that shape a child’s experiences and interactions. Bronfenbrenner’s theory encourages us to consider the broader ecological context in which children learn and grow.
Abraham Maslow (1908-1970)
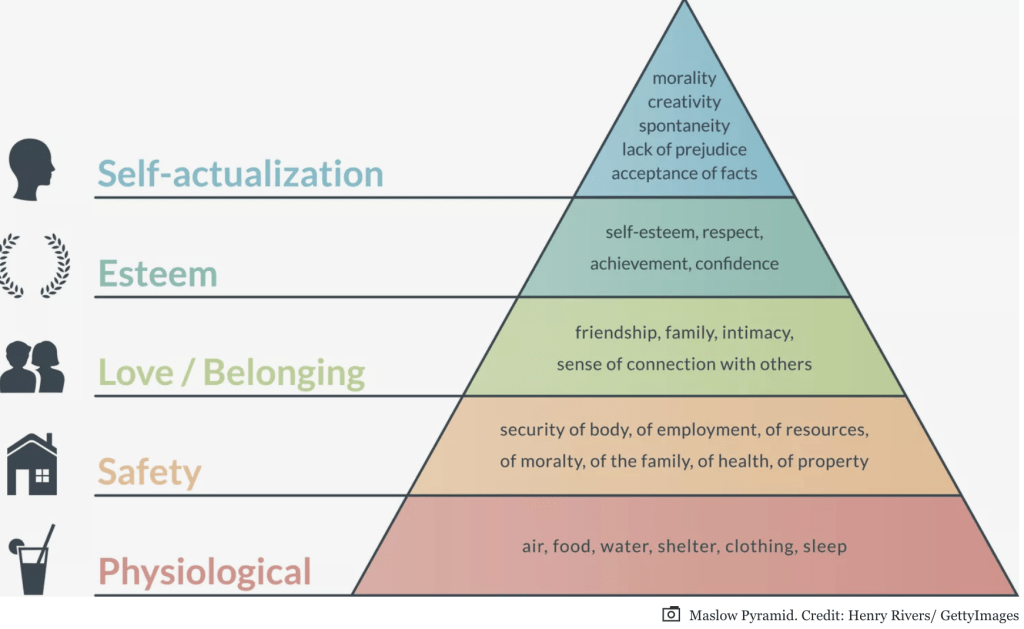
Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory is another significant contribution to the field of early years learning. Maslow proposed that individuals have a hierarchy of needs, starting with physiological needs such as food, shelter, and safety, and progressing to higher-level needs such as belongingness, esteem, and self-actualization. By considering Maslow’s theory, early years professionals can ensure that the fundamental needs of children are met, creating a supportive and nurturing environment that fosters their overall well-being and allows them to reach their full potential.
Theorists in your Kinderloop
By intentionally connecting a child’s learning experiences to theories, we can create meaningful and purposeful learning opportunities that align with their developmental needs and foster their overall growth. These connections allow us to implement strategies and provide environments that optimize children’s learning potential and support their individual learning journeys.
Ensure you tag your posts and observations with a ‘theorist learning outcome’ from the tags in your Kinderloop
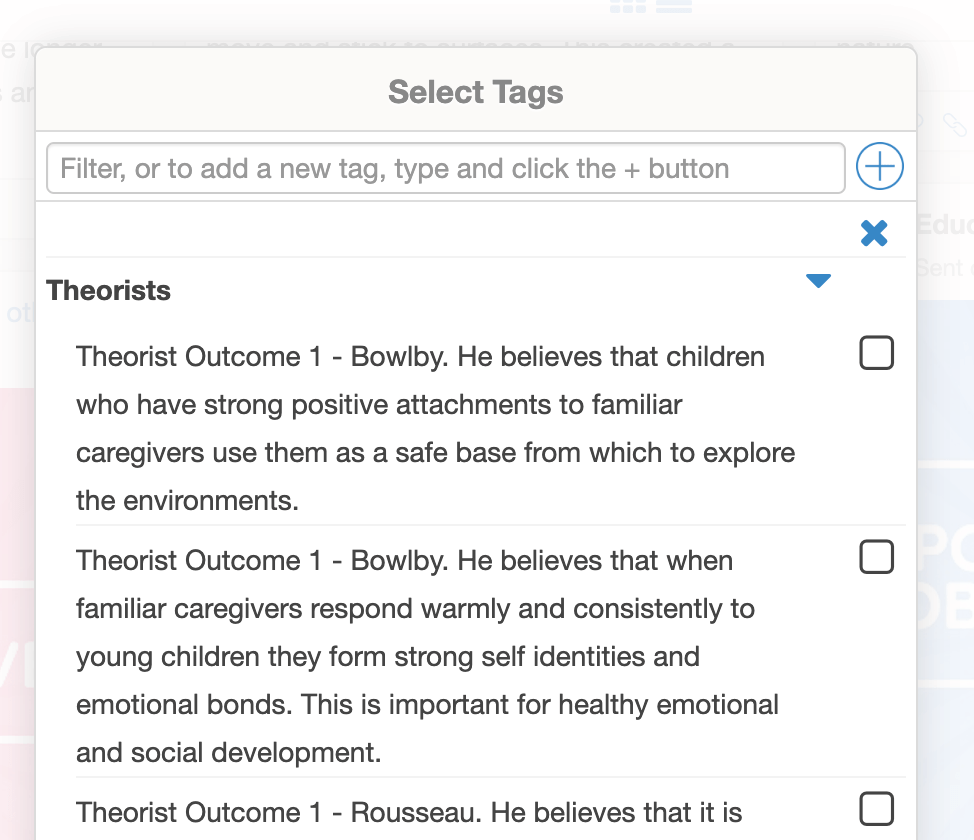
Add Theorsit Learning tags to your Kinderloop
If you haven’t yet added the Childhood Theoriests to your Kinderloop, you can do so by:
1/ Logging onto Kinderloop via the web (www.kinderloop.com)
2/ Go to settings > Learning tags
3/ Add more tags > Add theorists
You can also add in any extra theorist learning tags that you want to use by creating your own tags!
Happy Kinderlooping!
Follow along on our social pages to ensure you don’t miss out on all of the Kinderloop tips & hints, and learn about our new features!
Facebook
Instagram